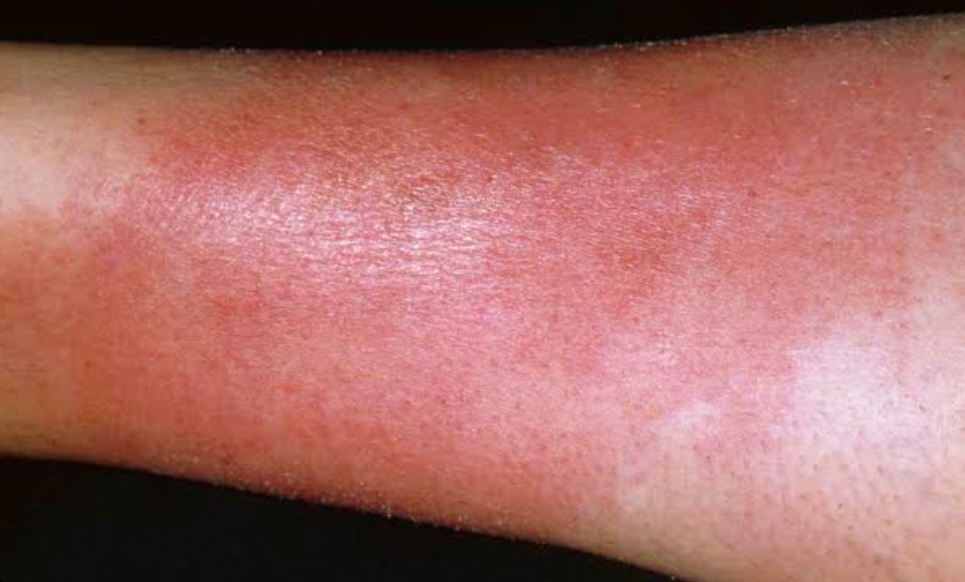
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and the underlying tissues. It is typically caused by bacteria, most commonly Streptococcus or Staphylococcus species, entering the skin through a break or crack in the skin's surface. The bacteria then multiply, leading to an infection.
Common symptoms of cellulitis include redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. The skin may also appear shiny and feel tender to the touch. In some cases, there may be a fever and swollen lymph nodes near the affected area.
Cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body, but it most commonly affects the legs, especially in the lower leg area. Factors that can increase the risk of developing cellulitis include:
Skin injuries or cuts
Pre-existing skin conditions like eczema or dermatitis
Impaired circulation, such as in individuals with diabetes or peripheral artery disease
Weakened immune system
Obesity
Intravenous drug use
Lymphedema (swelling due to impaired lymphatic system drainage)
Cellulitis is usually treated with oral or intravenous antibiotics to fight the bacterial infection. The choice of antibiotics depends on the severity of the infection and the specific bacteria involved. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional, even if symptoms improve, to ensure complete eradication of the infection.
Prompt medical attention is essential for cellulitis, especially if it is rapidly spreading, accompanied by high fever, or if there are signs of systemic illness. Complications of untreated or severe cellulitis can include the spread of infection to the bloodstream (sepsis), abscess formation, tissue death (gangrene), and long-term complications such as chronic swelling (lymphedema).
To prevent cellulitis, it is important to maintain good hygiene, keep the skin clean and moisturized, promptly treat any skin wounds or injuries, and practice proper wound care techniques.
More information for health professionals:
Consensus Guideline: Management of Cellulitis in Lymphoedema
Approved by the ALA Council June 2008; reviewed June 2010, March 2012, March 2015